Introduction to Operational Transfer Pricing
Operational Transfer Pricing, the mechanism for pricing the internal trading of goods and services within or among subsidiaries of organizations, was once relegated to a realm of cost accountants in charge of “trading wooden nickels”. It was considered to be an overall net zero-sum exercise for the organization. Over time though, intercompany transactions became a substantial work activity and a source of strategic value for performance and incentive management, as well as significant financial value through optimization of tax strategies. Substantial after-tax income could be influenced through the use of entities whose purpose was to allocate the profit margin on such an intra-enterprise business. Thus, were born complex corporate and legal structures and a commensurately large support structure of accountants, tax specialists, and lawyers.
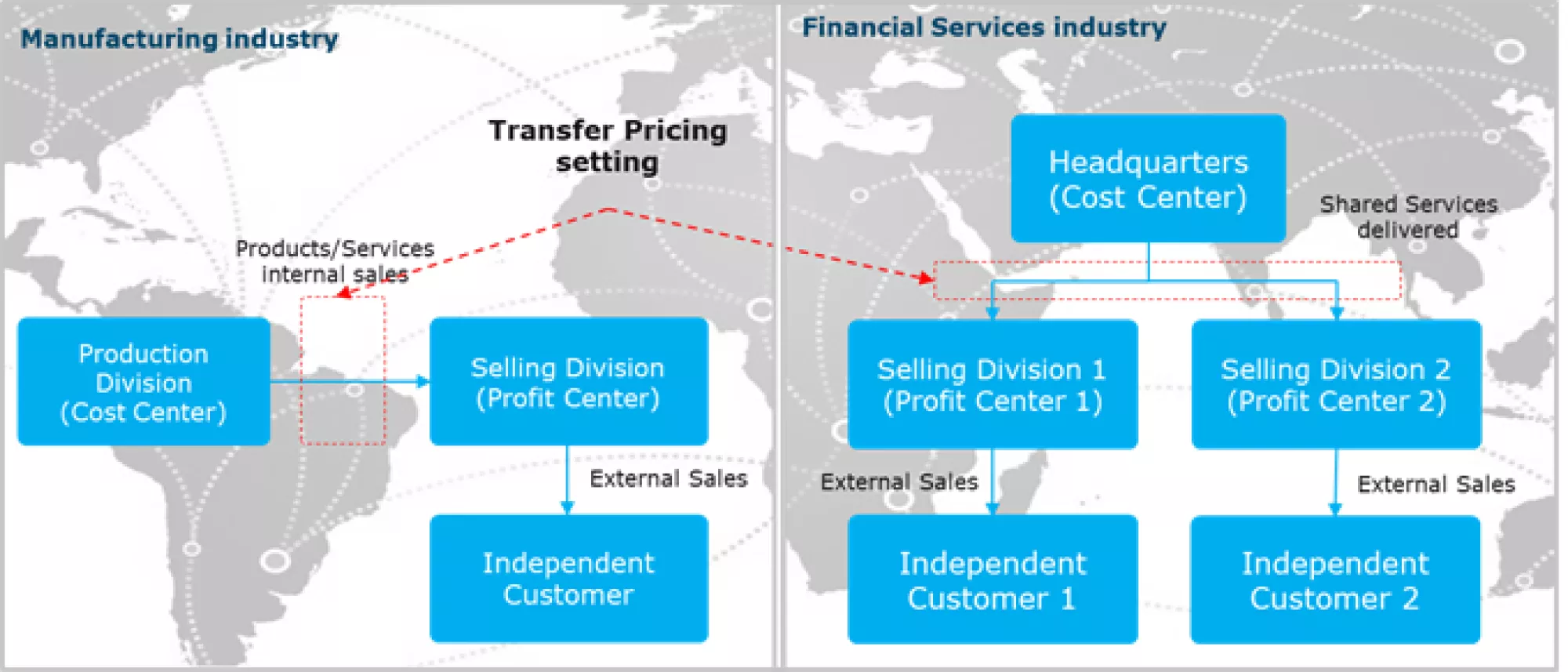
In more recent times, governments have been looking to protect revenue collection and minimize unproductive loopholes. This has led to an increase in the scrutiny of documentation and enforcement of transfer pricing regulations by their major tax authorities. Additionally, documentation must be contemporaneous to the time that tax returns are filed, and if audited, a company would have thirty days to provide such documentation.
Complicating the matter is the fact that inter-company transactions are dynamic, multi-directional, multi-national, and multi-currency. Multiple methodologies are needed to determine the pricing of intercompany business. Yet, a structured framework to calculate, document, and maintain these pricing relationships has been elusive and has become a priority for many organizations.
Operational Transfer Pricing Challenges
Companies implementing Operational Transfer Pricing in their organizations often struggle with the same set of challenges due to the need to incorporate multiple data sources, the introduction of foreign exchange complexity, Transfer Pricing methodology complexity, lack of reporting capability, and overall lack of transparency and audibility.
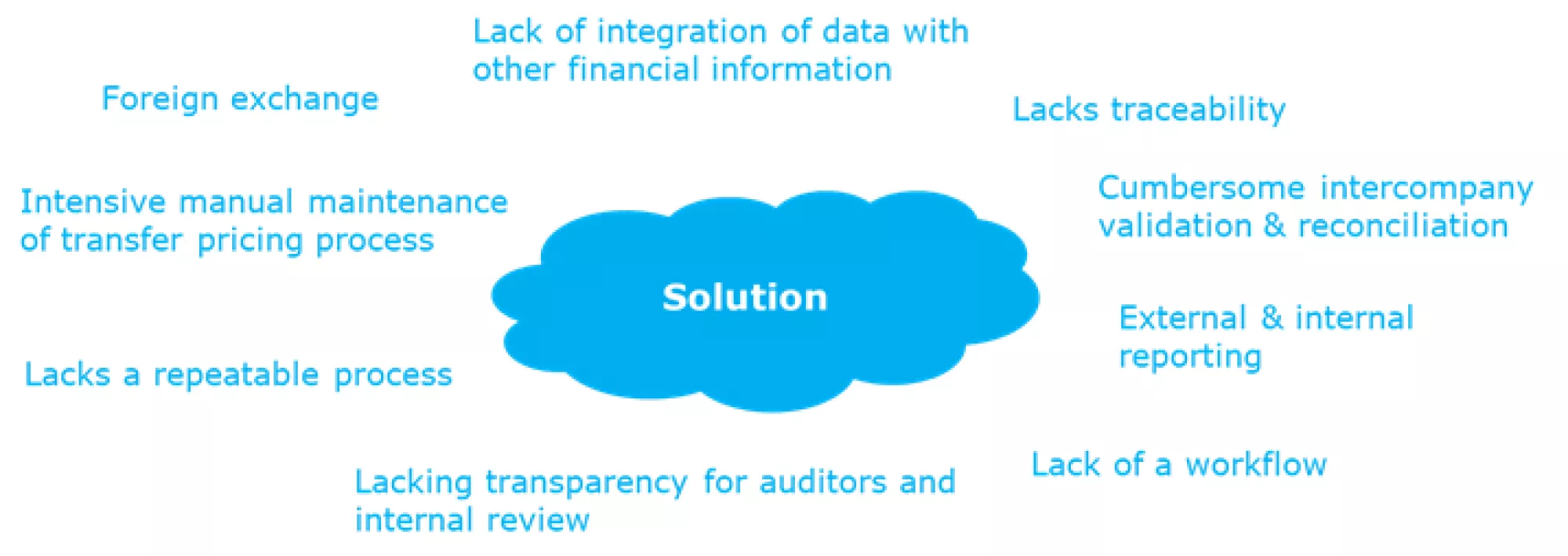
Many of these challenges are born out of the choice of implementation technology and applications. All too often, organizations implement custom OTP solutions that involve Microsoft Excel, Access, custom SQL Databases, or even an attempt to implement the solution in General Ledger itself. Although these solutions work in the short-term, they almost always lack the key requirements to ensure longevity for the solution.
To combat these challenges, an organization needs to ensure that the OTP solution implementation is:
- Infallible - Data Assurance and metadata management results in the solution being consistent, traceable and reliable.
- Dynamic - Allows for the flexibility to accomodate ever changing business requirements without excessive effort.
- Efficient - Increases speed and frequency of calculations, analysis and creation of invoices and journals through automated integrations, easy to understand rules, and enhanced reporting
- Auditable - Transparency of allocations and calculations through advanced reporting in multiple formats.
- Strategic - Alignment of application skillset and powerful reporting to quickly analyze results and identify variances, which lead to corrective action.
Implementing OTP In the Cloud
Regardless of the OTP technology and overall solution, all OTP solutions follow the same overall process. The before mention challenges present themselves at the various process steps if the right tool for the job is not utilized.
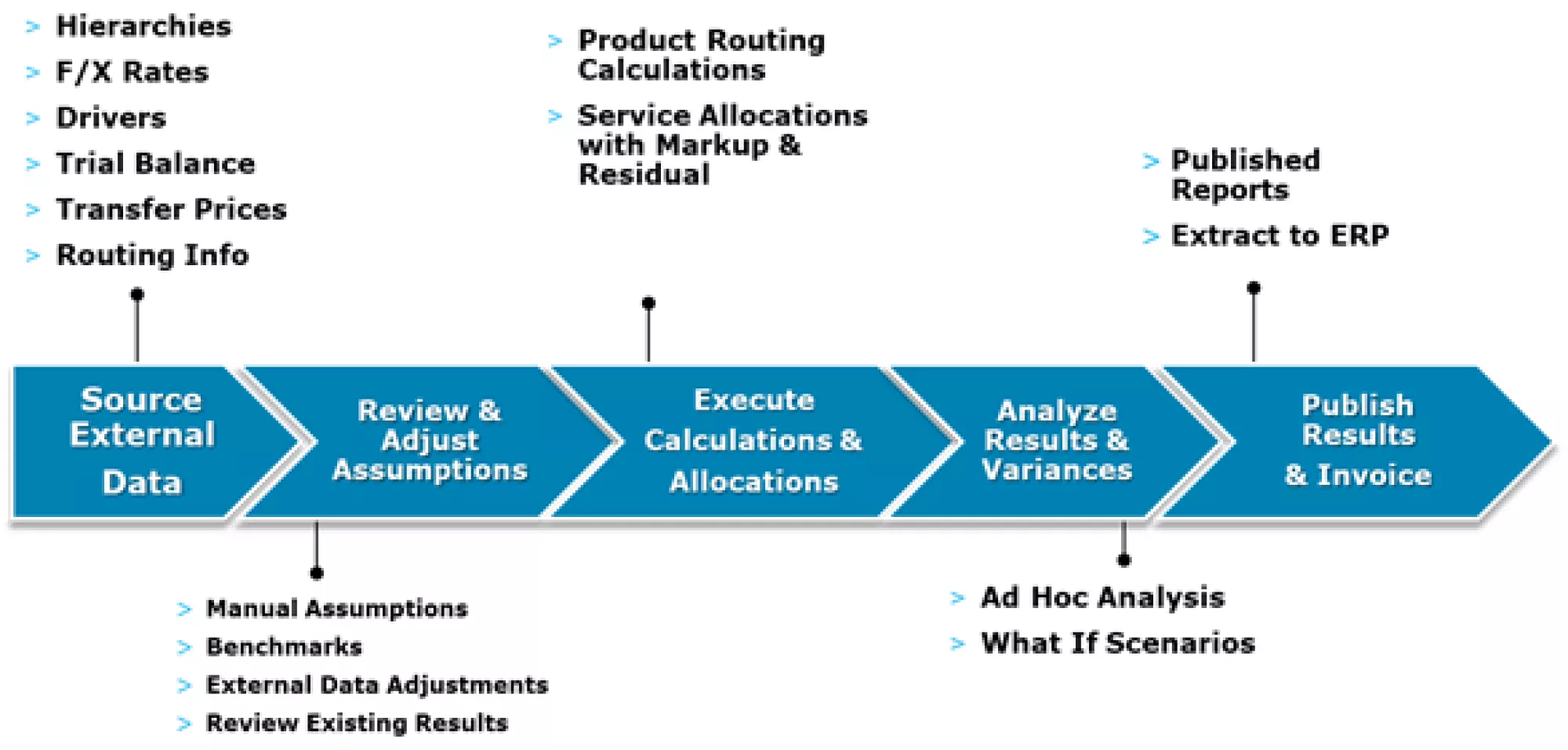
The below high-level solution architecture has been utilized by Alithya at numerous clients with great success.

Conclusion
In its own right, OTP can often be challenging, complicated, and, at times, confusing. Implementing an OTP solution in an inappropriate or ill-suited technology adds to these challenges and can result in organizations either feeling overwhelmed by their OTP solution and\or not being able to deliver specific mandatory requirements resulting in potentially devastating consequences.
The Oracle Cloud, and Oracle Cloud Enterprise PCM specifically, can assist organizations in delivering their OTP results in a solution that is easily deployed, understood, easily maintained, traceable and auditable.
For comments, questions, or suggestions for future topics, please reach out to us at [email protected]. Visit our blog regularly for new posts about Cloud updates and other Oracle Cloud Services such as Planning and Budgeting, Financial Consolidation, Account Reconciliation, and Enterprise Data Management. Follow Alithya on social media for the latest information about EPM, ERP, and Analytics solutions to meet your business needs.
